Fun Facts About Trigonometry
History of Trigonometry
Trigonometry began over 4,000 years ago with ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians, who used early forms of triangle measurements for astronomy and construction.
The ancient Greek mathematician Hipparchus (190–120 BC) is often called the Father of Trigonometry. He created the first known trigonometric table.
The word “trigonometry” comes from the Greek words trigonon (triangle) and metron (measure).
Indian mathematicians such as Aryabhata and Brahmagupta introduced early versions of sine and cosine functions centuries before they appeared in Europe.
Islamic scholars during the Golden Age, like Al-Battani and Al-Khwarizmi, expanded trig identities and used trigonometry for precise astronomical calculations.


Real-World Applications
Architecture & Construction: Used to determine heights of buildings, roof angles, and structural load calculations.
Astronomy: Helps measure distances between planets and calculate orbits.
Music & Sound Waves: The shapes of sound waves are sinusoidal, making trig essential for analyzing audio signals.
Physics & Engineering: Used to model motion, forces, and oscillations.
Geography & Navigation: GPS systems use trigonometry to calculate your position using satellite signals.
Medical Imaging: CT scans and MRIs rely on trigonometric algorithms to create detailed images of the body.
Computer Graphics: Video games and CGI use trig to rotate objects, create lighting effects, and animate characters realistically.
Famous Mathematicians
Hipparchus — Created the first trigonometric table and introduced chord functions.
Ptolemy — His Almagest contained trigonometric theorems and models of planetary motion.
Aryabhata — Introduced early sine tables and advanced trigonometric ideas in ancient India.
Al-Battani — Refined trigonometric identities and introduced the concepts of sine, cosine, and tangent as we use them today.
Leonhard Euler — Developed Euler’s Formula, e^(ix) = cos x + i sin x, one of the most elegant equations in mathematics.

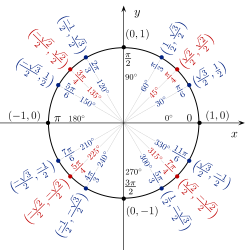
Interesting Patterns in the Unit Circle
All the coordinates on the unit circle follow the pattern: (cos θ, sin θ).
Values repeat symmetrically in each quadrant, which helps make trig functions periodic.
The angles 30°, 45°, and 60° produce special right triangles with simple square-root relationships.
The unit circle shows that sine and cosine represent the coordinates of a rotating point.
Reference angles explain why trigonometric values repeat in predictable cycles.
Use in Modern Technology
Smartphones: Use trigonometry for orientation sensors and motion tracking.
GPS Navigation: Depends on trigonometric calculations between satellites and Earth.
Virtual Reality (VR): Uses trig to track head position and adjust displays.
3D Animation: Uses trig to rotate objects and simulate motion.
Robotics: Uses trigonometry to calculate joint angles and movement paths.
Wireless Communication: Uses trig to model signal behavior and interference.
